

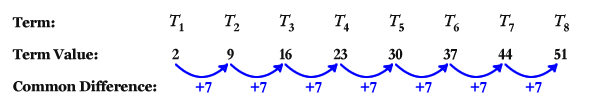
The arithmetic sequence formula is given as, an=a1+(n−1)d a n = a 1 + ( n − 1 ) d where, an a n = a general term, a1 a 1 = first term, and and d is the common difference. If you take any number in the sequence then subtract it by the previous one, and the result is always the same or constant then it is an arithmetic sequence. How can you say that a sequence is an arithmetic sequence?Īn arithmetic sequence is a list of numbers with a definite pattern.
Remember, a function is any formula that can be expressed as ” f(x) = x” format, but a sequence only contains integers at or greater than zero. What is the difference between a sequence and function? The only major difference between the two graphs is that an arithmetic sequence is discrete while a linear function is continuous. So arithmetic sequences are very much like linear functions, with the common difference playing the same role as the slope. How are graphs of arithmetic sequences and linear functions similar and different? Are linear functions arithmetic sequences?Īrithmetic Sequence vs Linear Function The difference between arithmetic sequence and linear function is that an arithmetic sequence is a sequence of numbers increasing or decreasing with a constant difference whereas a linear function is a polynomial function. If the term-to-term rule for a sequence is to add or subtract the same number each time, it is called an arithmetic sequence, eg: Arithmetic sequences are also known as linear sequences because, if you plot the position on a horizontal axis and the term on the vertical axis, you get a linear (straight line) graph. Is linear sequence and arithmetic sequence the same? 28 SOLVED:Describe the similarities and differences between arithmetic sequences and lincar functions.27 Partial Sum of an Arithmetic Sequence.24.4 More Problems Involving Arithmetic Sequences.24.1 Arithmetic sequences and linear equations.24 Arithmetic Sequences and Linear Equations.23 Arithmetic Sequences and Linear Functions.22.2 Example: Solving Application Problems with Arithmetic Sequences.22 Solving Application Problems with Arithmetic Sequences.21.3 Example: Finding the Number of Terms in a Finite Arithmetic Sequence.21.1 How To: Given the first three terms and the last term of a finite arithmetic sequence, find the total number of terms.21 Find the Number of Terms in an Arithmetic Sequence.20.10 How To: Do we have to subtract the first term from the second term to find the common difference?.20.9 Example: Writing a Recursive Formula for an Arithmetic Sequence.20.7 How To: Given an arithmetic sequence, write its recursive formula.20.6 A General Note: Recursive Formula for an Arithmetic Sequence.20.4 Example: Writing then th Term Explicit Formula for an Arithmetic Sequence.20.3 How To: Given the first several terms for an arithmetic sequence, write an explicit formula.20.2 A General Note: Explicit Formula for an Arithmetic Sequence.


6 How do you find the arithmetic sequence?.5 How can you say that a sequence is an arithmetic sequence?.4 What is the difference between a sequence and function?.3 How are graphs of arithmetic sequences and linear functions similar and different?.2 Are linear functions arithmetic sequences?.1 Is linear sequence and arithmetic sequence the same?.Jungnickel, "Finite fields: Structure and arithmetics", Bibliographisches Inst. Blahut, "Theory and practice of error control codes", Addison-Wesley (1983)ĭ. Consequently, a periodic binary sequence with good randomness properties should have complexity close to the period length and a profile growing more or less smoothly. For a shift register sequence $\mathbf$ with period $N$ results in a linear complexity close to $N$, provided that $N$ is a power of $2$ or a Mersenne prime number (cf.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
